eM Cube Distributed Accelerator (Code: DISAC)
General Scope
Distributed Accelerator developed by eM Cube has very much different structure from the traditional accelerators in the market. eM Cube defined accelerator as a process and as shown figure 1 below.
- Figure 1. Process Definition of Ion Particle Accelerator

eM Cube implemented the process automation technologies into the accelerator to optimize its process.
Specification
The biggest advantage of the distributed accelerator is "acceleration efficiency" which about 10 times high compared to the traditional high energy accelerators. It expands the accelerator applicable scope where not used by the limitations of relative balance of energy produced.
- Chart 1. Comparative Table
-
Accelerator Type Electrical Field
Gen. MethodBeam Orbit Acceleration
EnergyEfficiency *1 Cyclotron High Freq. Spiral 100Mev 5% Synchrocyclotron High Freq. Spiral 500Mev 3% Synchrotron High Freq. Circular 50GeV 2% LINAC High Freq. Linear 400MeV 5% Distributed Accelerator
(DISAC)Full Digital Control Linear & Circular 430Me 60%<
Efficiency *1:
If the particle accelerated to 400MeV by the beam average current 1mA by the accelerator with 5% efficiency, the consumption energy of the accelerator is;
1mA * 400MV / 5% = 8MW
And if the same acceleration is done by the distributed accelerator, the energy will be;
1mA * 400MV / 60% = 0.67MW
Therefore the performance will be much more than 10 times.
Acceleration Method
Figure 2 shows the traditional acceleration method.
Induce the high frequency voltage in to the tube, the high acceleration energy is generated by keep providing electrical field in acceleration during the charged particle passes the acceleration gap.
- Figure 2. Traditional Acceleration Method
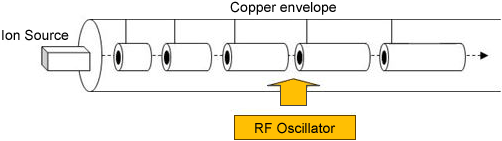
Figure 3 shows the acceleration method of the Distributed Accelerator.
Without using the high frequency voltage, the high acceleration energy is generated by control module switching the tube electrical potential during the charged particle passes the acceleration gap
- Figure 3. Distributed Acceleration Method
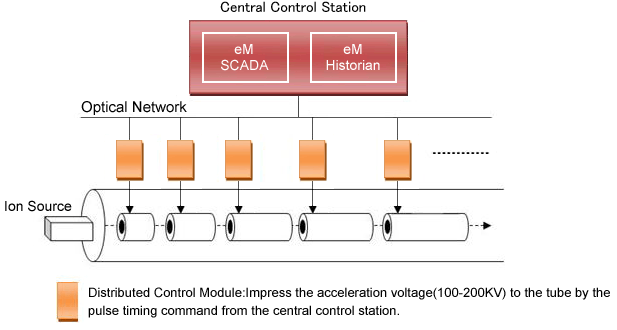
eM SCADA Functionality
A concept of Tags in the process automation is used in the distributed accelerator to efficiently manage its control information. As shown in the figure 4, the process information of ion beam pulses discharged from ion source is managed as TAG. Ion beam pulses are discharged every 20 micro seconds therefore the central control station requires to process 500,000 tags every second. eM-SCADA is a general purpose SCADA platform however eM Cube has a solution combined with our controller to process it.
- Figure 4. TAGs in the Distributed Accelerator
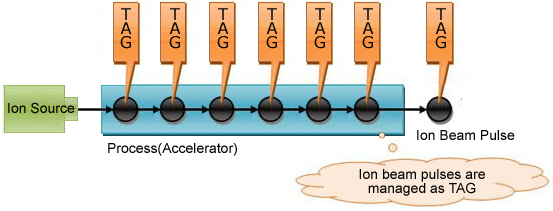
Here is a brief information of Process TAGs:
- 《TAG consists of the following information》
-
- SV (Setting Value)
- Ion beam frequency/duration, applied voltage switch timing, voltage output etc.
- MV (Manipulated Value)
- Actual value measured vs. SV.
- PV (Process Value)
- Ion beam pulse velocity, time gap passed, electrical charge and density, vacuum degree, etc.
- SV (Setting Value)
eM-SCADA is used to manage robust supervisory control of the acceleration control based on TAG information. All process information of ion beam pulses are monitored in real-time and in the case of error the information is used to execute the emergency sequences to avert the negative impact to the system. The robust supervisory control makes distributed accelerator to minimize the radiation risks and helps cost savings for safety and facility construction.
eM-Historian Functionality
eM-Historian is used to log all TAG process information and statistically analyze system safety in real and historically for the condition based maintenance. eM-Historian send the maintenance request to the operators based on the conditions set such as deviation limit of process value change and helps to save the maintenance cost for the system..
- Figure 5. Routine Maintenance
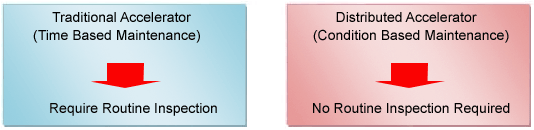
eM Cube improved the standard functionality of eM-Historian to have logged all process TAG information from the distributed accelerator particles to improve quality of process of the control system.
Scope of Supply
Chart 2. shows the major components of Distributed Accelerator and ★ indicates the components may sourced from other than eM Cube Corporation however we consult through the discussion.
- Chart 2. Scope of supply matrix
-
Major Components Supply Supervisory Control Station Hardware ★ Software ★ Distributed Control Module Hardware ★ Software ★ Networking Components ★ Electrode Tube for Beam Chopper ★ Main Accelerator ★ Defecting Magnet ★ Ion Source ★ Vacuum Equipments ★
★ : supplied by eM Cube Corporation.
★ : may supplied by eM Cube business partners.
Summary
The traditional accelerators are used more like R&D purposes specially in the energy or medical domains where requires need to deal with high RAS (Reliability, Availability, Serviceability) requirements made users difficult on cost for construction, operation and maintenance. eM Cube Corporation's "Distributed Accelerator" will make a innovative change with this PATPEND technologies and we believe this will extend its usage to new applications in the near future.
- ※
- Please contact Sales Department for inquiries or R&D Department for further information of eM Cube products.







